Electro Oxidation Basics#4: Why Choose BDD Electrode Over titanium dioxide electrode
BDD Electrode Vs. Titanium Dioxide Electrode: Choose Anode Materials for Wastewater Treatment
When it comes to electro oxidation, an innovative approach out of Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes (EAOPs) adopted to treat wastewater, the choice of electrodes, especially anode, is not another technical detail within the treatment processes, anode is one of the major elements that impact removal efficiency, oxidant generation, operation costs, mediated oxidation and byproduct formation, kinetic performance, then eventually your treatment efficiency and objectives.
There are two major anodes available to complete mineralization of persistent organic pollutants or effective electro oxidation industrial wastewater treatment solutions, Boron-Doped Diamond BDD electrode and titanium dioxide electrode. While both electrodes are implemented in wastewater treatment processes, they are fundamentally different in oxidation mechanisms and roles in different methods and technology.
Partial of the content regarding titanium dioxide electrode are inspired by Nanostructured titanium dioxide as novel electrodes for water/wastewater treatment
A Final Showdown: "Active" BDD Electrode vs. "Non-Active" Titanium Dioxide Electrode
In this part, we explore hydroxyl radicals generation, depth of oxidation, oxidation mechanisms of BDD electrode and titanium dioxide electrode, that is to indentify the key differences of these two anodes, and figure out why these electrodes are applied in different wastewater treatment processes.
Actual treatment efficiency of an anode is not just about the properties of the electrode material, how the electrode material interacts with the specific ions in your wastewater affect the results.
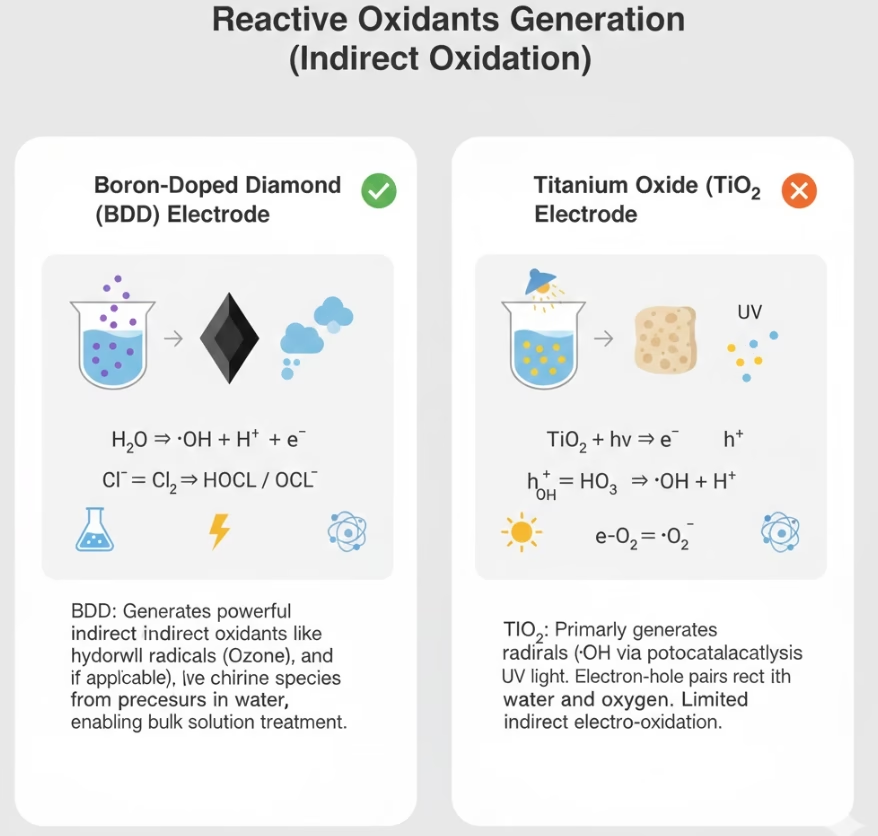
BDD Electrode Vs. Titanium Dioxide Electrode for Radical Generation
BDD electrode generation reactive radicals via direct anodic oxidation. It uses a massive electrochemical window up to some 1.8 to 2.3 v/SHE to “take” electrons from water molecules at the anode surface. Diamond anode is naturally non-reactive, it does not form a bond with the radicals it creates. A high concentration of “free” or weakly adsorbed hydroxyl radicals and other reactive oxidants are ready to attack anything in the electrolytes.
While titanium dioxide electrode typically operates via Photocatalysis which create an electric field to prevent electron-hole recombination. It requires light energy (UV) to excite electrons from its valence band to its conduction band. This creates “holes” (h+) that react with water to form radicals. These two anodes are quite different in indirect oxidation: BDD electrode function as main spots for radicals, while titanium dioxide electrode does not.
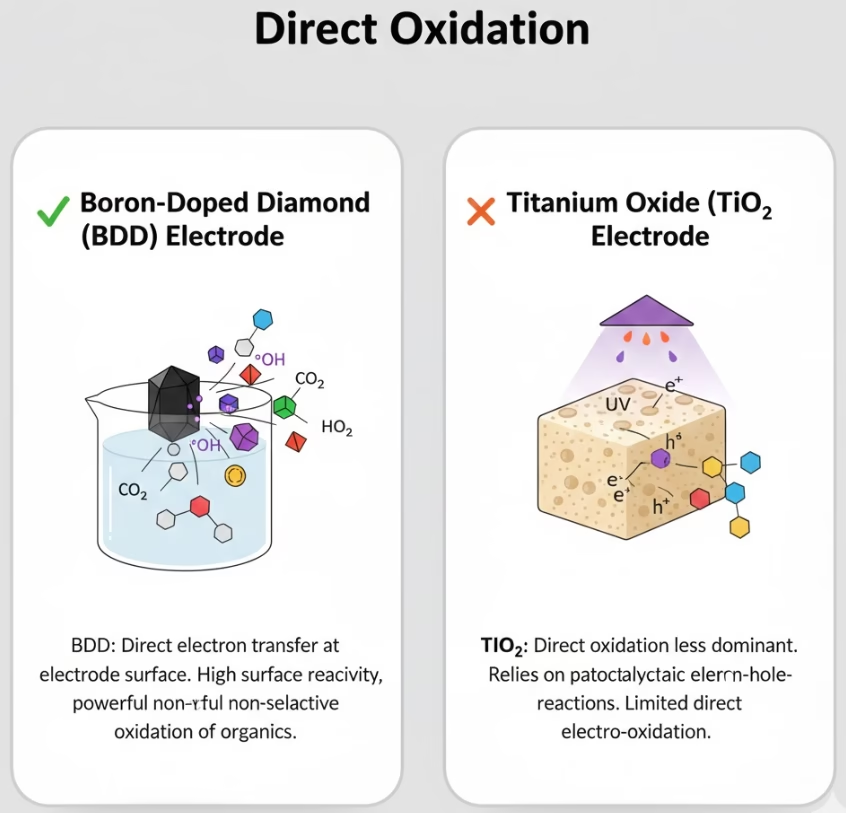
Titanium Dioxide Electrode Vs. BDD on Depth of Oxidation & Mineralization
Organic molecules don’t adhere strongly to the diamond lattice, as a non-active electrode, the surface of BDD electrode doesn’t get fouled as easily by polymerizing byproducts. Oxidation happens in the Helmholtz layer immediately adjacent to the surface, It resists the simple oxidation of water into oxygen gas for its high oxygen evolution overpotentials, aka a high “electrochemical pressure.” That’s to strip electrons from almost any organic bond. In direct oxidation, BDD is capable of stripping down a complex molecule to CO2 and water in a single, rapid sequence of steps at the anode surface.
Direct oxidation with titanium dioxide electrode is often referred to as “hole-driven oxidation” (h+). When light or voltage creates a hole in the valence band, a pollutant molecule must physically interact with that site. it can be more “selective” for oxidation of certain functional groups, which reflects partial diret oxidation, breaking specific bonds, instead of mineralization as titanium dioxide electrode has much lower potentials.

Water Matrixs & Anode Selection
In chloride-rich water, influential hydroxyl radicals generated from BDD electrode can oxidize chloride into Perchlorates which have significant impact for drinking water and sensitive ecosystems. TiO2 titanium dioxide electrode and its derivatives., e.g, RuO2-TiO2 are excellent catalysts for Chlorine evolution reaction which mainly generate active Chlorines, e.g, HOCL/OCL- instead of perchlorates. Ions such as Bicarbonates and Carbonates are radical scavengers form carbonate radicals which is a group of radicals with weaker oxidation capability than hydroxyl radicals, main reactive oxidants of rely more on direct hole (h+) oxidation, which is slightly more resistant to bicarbonate interference.
Anode selection amongst BDD and titanium dioxide electrode is mainly about your goal: full mineralization or partial removal? Does the water contain high levels of Chloride? Budget/estimated cost?Anode lifespan requirement? Not determind yet? Reaching out to our engineering team with 20 years of experiences solve this problem.
Titanium Dioxide Electrode Vs. BDD Electrode for Treatment of Real Wastewater
A final showdown of boron doped diamond BDD electrode vs.TiO2 titanium dioxide electrode in treatment of real wastewater, how does these two anodes perform in COD and TOC removal, and then a comparative comparison of these two electrodes.

COD Degradation Efficiency Comparison of BDD vs. Titanium Dioxide Electrode
Chemical Oxygen Demand reflects organic load of your waste streams, therefore we run a comparison of titanium dioxide electrode and BDD electrode on COD degradation efficiency. Specific wastewater characteristics, treatment goals, and economic consideration are the key elements to consider under this scenarios.
BDD electrode is the optimal anode with maximum COD degradation efficiency, unpaired ability to generate reactive hydroxyl radicals that mineralize persistent organic pollutants, especially challenging, highly concentrated, complex industrial wastewater requiring complete mineralization.
Titanium dioxide electrode offer a more cost-effective solution for specific applications, especially when combined with UV light, mainly provide lower COD removal rates and usually lead to partial degradation.

Final Showdown: TiO2 Titanium Dioxide Electrode and BDD electrode
Neither electrode is universally “superior.” BDD electrode offers unmatched performance, higher current efficiency, durability, and mineralization potential for applications of treatment of complex industrial wastewater with persistent organic pollutants such as active pharmaceutical ingredients, aromatic compounds, personal care products, aromatic compounds, e,g,Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs), Phenolic Compounds, pesticides, industrial chemicals, and etc, yet with a much higher upfront capital investment.
With a lower intial cost, TiO2 titanium dioxide electrode provides a more cost-effective, versatile application in photocatalyst or say photo-electrocatalytic system, usually relies on lights, significantly slash toxicity and enhance biodegradability, then easing the load on subsequent biological treatment, ideal for partial degradation, less stringent treatment goals, pre-treatment, or specific pollutant removal, especially in systems where its catalytic properties can be optimized.
The selection is a sophisticated balancing act, weighing these diverse perspectives to align with specific project goals, budget, and environmental regulations.
Questions about electrode material? Get started to reaching out to us now.
It's strategic decision balancing upfront investment against long-term operational performance and environmental compliance of different electrode materials.